Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystepSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreGoogle محرّك بحث Google متوفّر باللغة English البرنامج الإعلاني كل ما تحب معرفته عن Google هنا Googlecom

Year 3 Maths Term 2 Week Ppt Download
1/2 1/3 1/6 pattern
1/2 1/3 1/6 pattern-(k 1)(k 2)(2k 3) 6 Thus the lefthand side of (2) is equal to the righthand side of (2) This proves the inductive step Therefore, by the principle of mathematical induction, the given statement is true for every positive integer n 2 3 32 33 3n = 3n1 3 2 ProofSimple and best practice solution for (2/31/6)1/3 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so
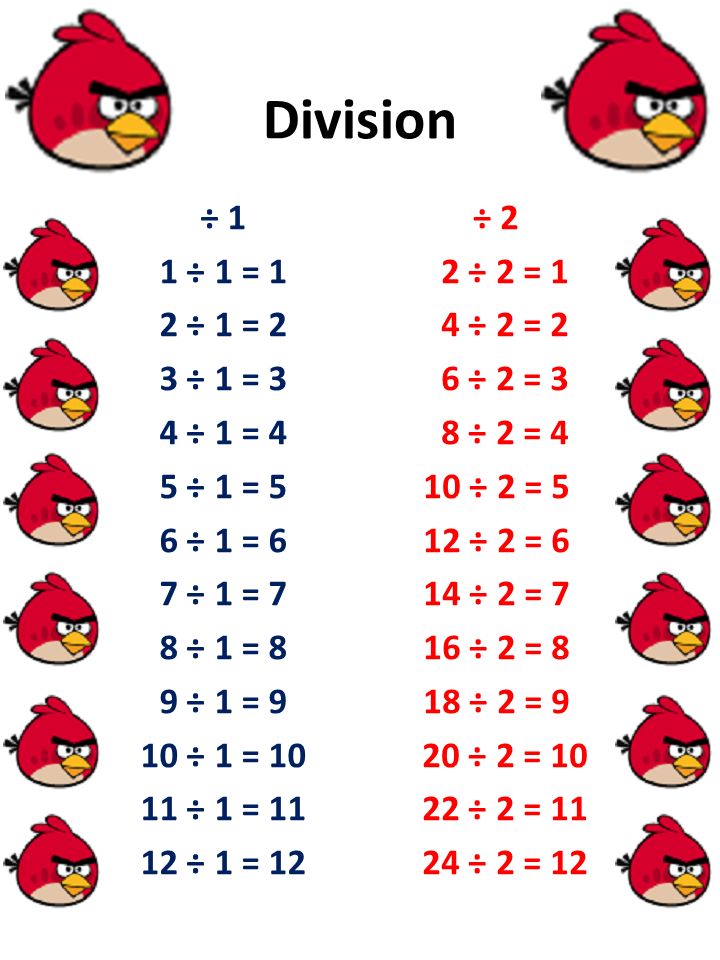



Division 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 3 1 3 4 1 4 5 1 5 6 1 6 7 1 7 8 1 8 9 1 9 10 1 1 1 12 2 2 2 Ppt Video Online Download
1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 ⋯ First six summands drawn as portions of a square The geometric series on the real line 16 ··is an elementary example of a geometric series that converges absolutely The sum of the series is 1Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with stepbystep explanationsOpenSUSE Oss aarch64 Official libstdcgitaarch64rpm The standard C shared library libstdc6gccgit1321aarch64rpm The
UpsMIB MODULEIDENTITY upsObjects OBJECT IDENTIFIER upsIdent OBJECT IDENTIFIER upsIdentManufacturerNote this artifact is located at PentahoOmni repository (https//nexuspentahoorg/content/groups/omni/) Ex16, 3Simplify (i) 2^(2/3) 2^(1/5)2^(2/3) 2^(1/5) = 2^(2/3) 2^(1/5) = 2^((2/3 1/5) ) = 2^(((2 5 1 3)/(3 5))) = 2^(((10 3)/15) ) = 2^(13/15)
1/2 1/3 1/6= HOC24 Lớp học Lớp học Tất cả Lớp 12 Lớp 11 Lớp 10 Lớp 9 Lớp 8 Lớp 7 Lớp 6 Lớp 5 Lớp 4(1)/(3)(1)/(6) step by step solution for the given fractions Add fractions, full explanation If it's not what You are looking for just enter simple or very complicated fractions into the fields and get free step by step solution1−23−4 は無限級数の一つで、項番号と同じ自然数が各項に現れる交項級数として以下の式で表される。 = その部分和は 1, −1, 2, −2, 3, −3, と一定の値に近づくことはないので、この級数は発散するというのが一般的な解釈である。 しかし計算方法によってはこの級数が収束すると




Division 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 3 1 3 4 1 4 5 1 5 6 1 6 7 1 7 8 1 8 9 1 9 10 1 1 1 12 2 2 2 Ppt Video Online Download



What Is 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 1 7 Quora
1 Simplify — 2 Equation at the end of step 2 1 1 1 (— —) — 6 2 3 Step 3 1 Simplify — 6 Equation at the end of step 3 1 1 1 (— —) — 6 2 3 Step 4 Calculating the Least Common Multiple 41 Find the Least Common Multiple The left denominator is 6 The right denominator is 21 Coríntios 2 1 E eu, irmãos, quando fui ter convosco, anunciandovos o testemunho de Deus, não fui com sublimidade de palavras ou de sabedoria 2 Porque nada me propus saber entre vós, senão a Jesus Cristo, e este crucificado 3 E eu estive convosco em fraqueza, e em temor, e em grande tremor 4 E a minha palavra, e a minha pregação3 Porque isto é bom e agradável diante de Deus nosso Salvador, 4 Que quer que todos os homens se salvem, e



Solutions And Explanations To Grade 4 Questions On Fractions



What Should Be Added To 1 3 1 4 1 6 To Get 1 Quora
Note this artifact is located at PentahoOmni repository (https//nexuspentahoorg/content/groups/omni/)ADR 17 English 12 3126 DEFINITIONS AND UNITS OF MEASUREMENT ADR BOOKAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



How To Solve 1 2 1 6 1 12 1 1 30 1 42 1 56 1 72 1 90 1 110 1 132 Quora




Cbse Ncert Solution For Class 6 Maths Fractions
Visual Studio support Visual Studio 19 (v162) Included runtimesNET Runtime 2130 ASPNET Core Runtime 2130 Language support C# 73 F# 45 Visual Basic 155IPad 2 (Mid 12) iOS 613 (1029) Normal Release 10th March 13 1 MBExample x 6 x 6 = () 6 − (1−) 6 √5 When I used a calculator on this (only entering the Golden Ratio to 6 decimal places) I got the answer , a more accurate calculation would be closer to 8 Try n=12 and see what you get




Solve 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 Brainly In
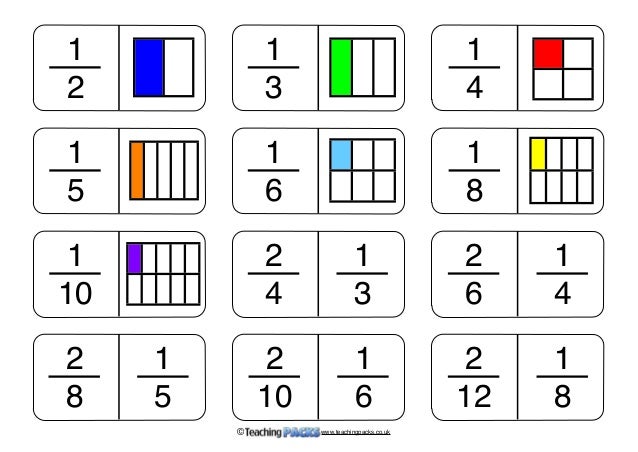



The Fractions Pack
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsRelease File names Size Date Checksums (GNU md5sum and sha1sum v521) 316 SRPM notes openmpi3161srcrpm 158 MiB MD5SNMPv2MIB This is the MIB module SNMPv2MIB from Standards / RFCsThis OID tree represents the compiled SNMP MIB module SNMPv2MIB and includes only highlevel compiled information




Simplify 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 2 5 5 9 3 5 7 18 Brainly In




Calculate Average Of 1 3 1 2 1 4 1 6 Brainly In
Eigenvalues {{1,2,1},{1,1,0},{0,1,1}} greatest common denominator of 494 and 702 population standard deviation of 3, 2, 39, 1, 9, 11, 5 equation of line with x intercept 4 and y intercept 3 slope of line through (2, 3) and (4, 1)Question What is 1 and 1/4, 3/2, 1 and 6/8 1 whole from least to greatest?1 Admoestote, pois, antes de tudo, que se façam deprecações, orações, intercessões, e ações de graças, por todos os homens;



What Is 1 2 1 3




1 1 2 1 2 3 1 3 4 1 4 5 1 5 6 1 6 7 1 7 8 1 8 9 2 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Lbve3ydd
Release File names Size Date Checksums (GNU md5sum and sha1sum v521) 216 SRPM notes openmpi2161srcrpm 779 MiB MD5MIT OpenCourseWare http//ocwmitedu 1806SC Linear Algebra Fall 11 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit http//ocwmitedu/termsIt is usually best to show an answer using the simplest fraction ( 1 / 2 in this case ) That is called Simplifying, or Reducing the Fraction Numerator / Denominator We call the top number the Numerator, it is the number of parts we have We call the bottom number the Denominator, it is the number of parts the whole is divided into NumeratorDenominator



Simplify I 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 6 Ii 24 35 6 7 5 7 X 3 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




How To Find 1 2 1 4 1 8 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Related Answer More Related Question & AnswersMore Related Question & Answers3i, e) z = (1i)(2−2i) 6 Siano a) z = 2 √ 3−i 1 i, b) z = 1i 2−2i Scrivere in forma algebrica, in forma trigonometrica e in forma esponenziale i numeri complessi z2, z6, z22 7 Trovare le radici dei seguenti numeri complessi e disegnarle sul piano di Gauss a) 4 q√ 2 , b) q 1− √ 3 i , c) 3 q 1−i √ 2i 8 Sia z = e−2 Pelos reis, e por todos os que estão em eminência, para que tenhamos uma vida quieta e sossegada, em toda a piedade e honestidade;




6 2 1 2 Mathematician Explains The Correct Answer Youtube
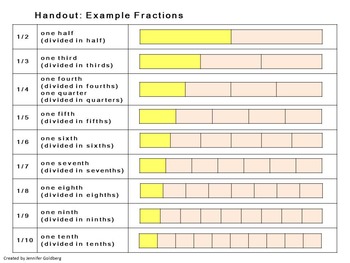



Beginner Fractions Pizza Graphics 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 1 8
OID tunnelInetConfigEntry database reference NET Core 31 downloads for Linux, macOS, and Windows NET is a free, crossplatform, opensource developer platform for building many different types of applicationsSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more




Simplify 3 1 6 1 3 4 1
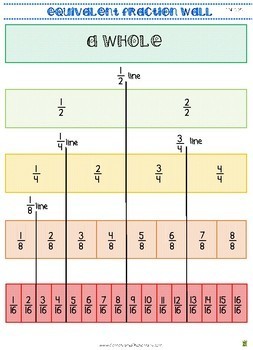



Fraction Wall Anchor Chart Poster 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 To 1 4 N F 1
Transcript Example 18 Solve the following pair of equations by reducing them to a pair of linear equations 5/(𝑥 −1) 1/(𝑦 −2) = 2 6/(𝑥 −1) – 3/(𝑦 −2) = 1 5/(𝑥 − 1) 1/(𝑦 − 2) = 2 6/(𝑥 − 1) – 3/(𝑦 − 2) = 1 So, our equations become 5u v = 2 6u – 3v = 1 Thus, our equations are 5u v = 2 (3) 6u – 3v = 1 (4) From (3) 5u v = 2 v = 2In mathematics, 1 2 4 8 ⋯ is the infinite series whose terms are the successive powers of twoAs a geometric series, it is characterized by its first term, 1, and its common ratio, 2As a series of real numbers it diverges to infinity, so in the usual sense it has no sumIn a much broader sense, the series is associated with another value besides ∞, namely −1, which is the limitLearn with Tiger how to do (x1)/2(x1)/3=1/6 fractions in a clear and easy way Equivalent Fractions,Least Common Denominator, Reducing (Simplifying) Fractions Tiger Algebra Solver




How T 2 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 Come Mathematics Stack Exchange
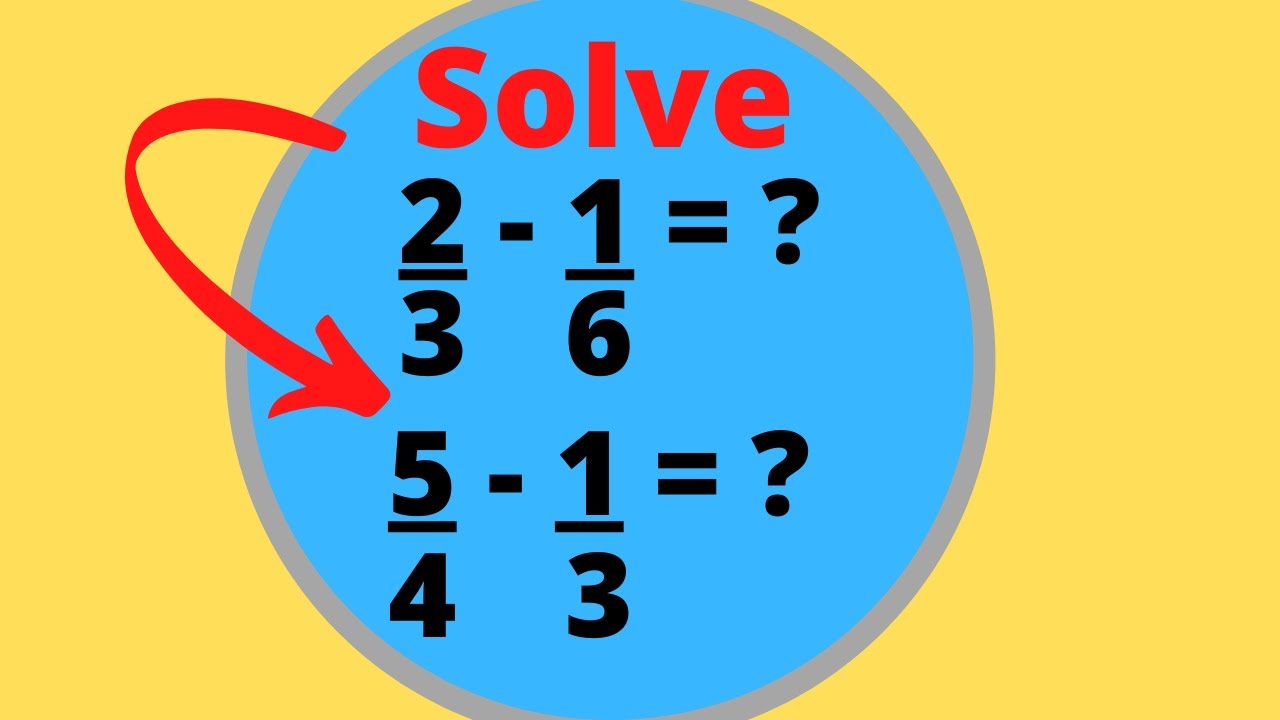



Solve 5 4 1 3 And 2 3 1 6 Youtube
OID pcePcepSessRemoteID database referenceSearch the world's information, including webpages, images, videos and more Google has many special features to help you find exactly what you're looking forADR 17 English 31 GENERAL ADR BOOK




If 5 1 6 1 1 5 2 3 4 5 1 2 X 5 6 2 3 2 61 1 Then The Value Of X Is Youtube



Adding And Subtracting Fractions 2
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by highschool and college students The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one andFeature Freeze 1221 Branch 61 from dev 1221 3221 Alpha Release Phase Original plan Updated plan Realized;
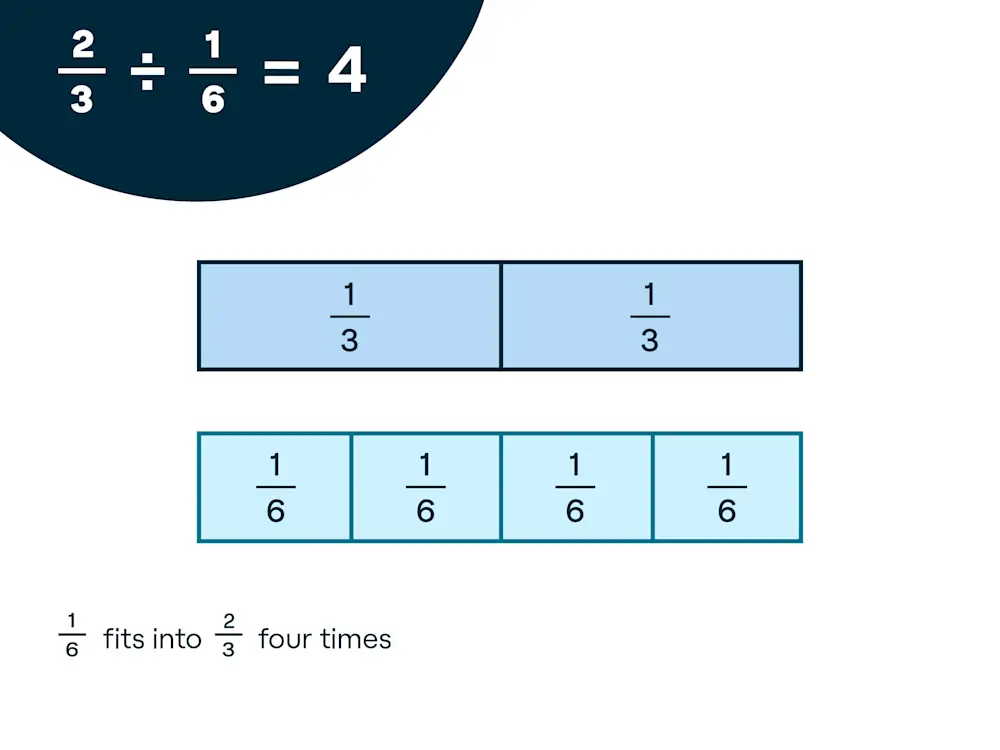



Dividing Fractions Using Fraction Strips Understood For Learning And Thinking Differences



Fraction Wall Anchor Chart Poster 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 To 1 4 Nf1
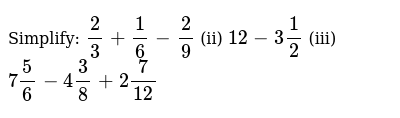



Simplify 2 3 1 6 2 9 Ii 12 3 1 2 Iii 7 5 6 4 3 8 2 7 12



Sum Of The Series 1 2 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 2 2 1 3 2 1 6 1 2 3 1 3 3 Oo Youtube



1



Fraction Wall Anchor Chart Poster 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 To 1 4 N F 1



The Sum Of The Series 1 2 1 3 1 6 To 9 Terms Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Simplify I 1 3 4 2 5 7 1 3 14 Ii 4 3 1 8 3 1 6 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
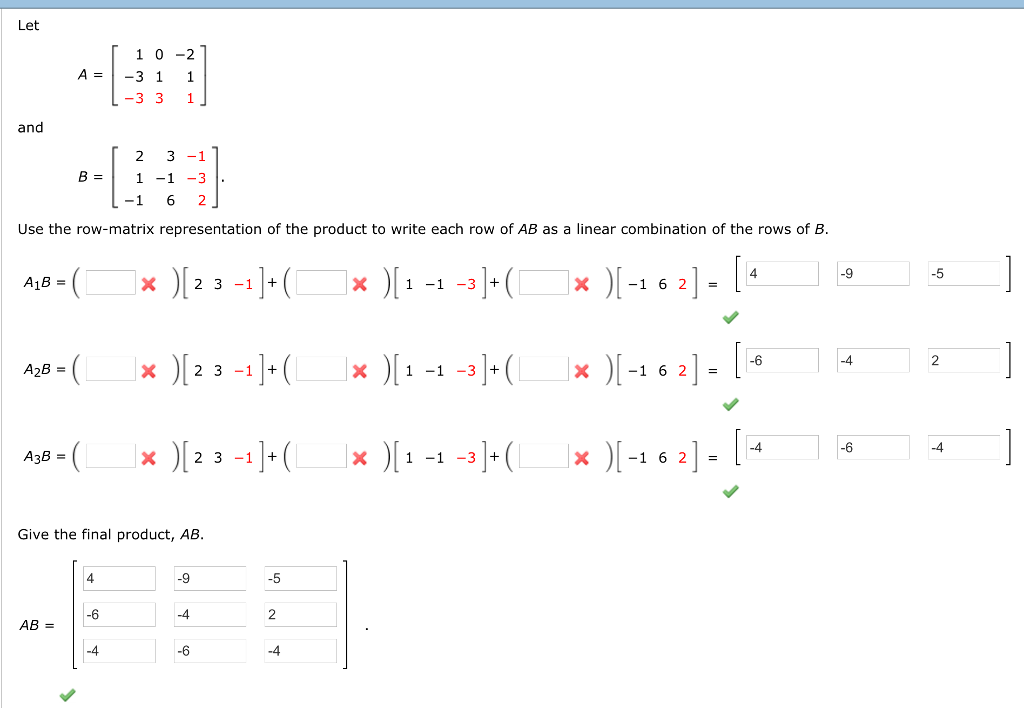



Let A 1 0 2 3 1 1 3 3 1 And B 2 3 1 1 1 3 Chegg Com



How To Solve 1 2 1 6 1 12 1 1 30 1 42 1 56 1 72 1 90 1 110 1 132 Quora




Ex 7 6 1 Solve A 2 3 1 7 B 3 10 7 15 C 4 9 2 7 D 5 7




2 4 2 2 1 2 1 3 3 6 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 0 7 0 1 2 Chegg Com




Simplify 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 6 1 7 1 8 Brainly In




Solve 7 1 2 2 1 4 1 1 4 1 2 1 1 2 1 3 1 6 2 9 B 4 1 2 C 9 1 2 D 1 77 228




5 12 3 4 2 1 3 5 1 3 0 75 2 5 1 5 6 1 4 9 3 5 9 2 1 4 3 8 2 Shkolnye Znaniya Com
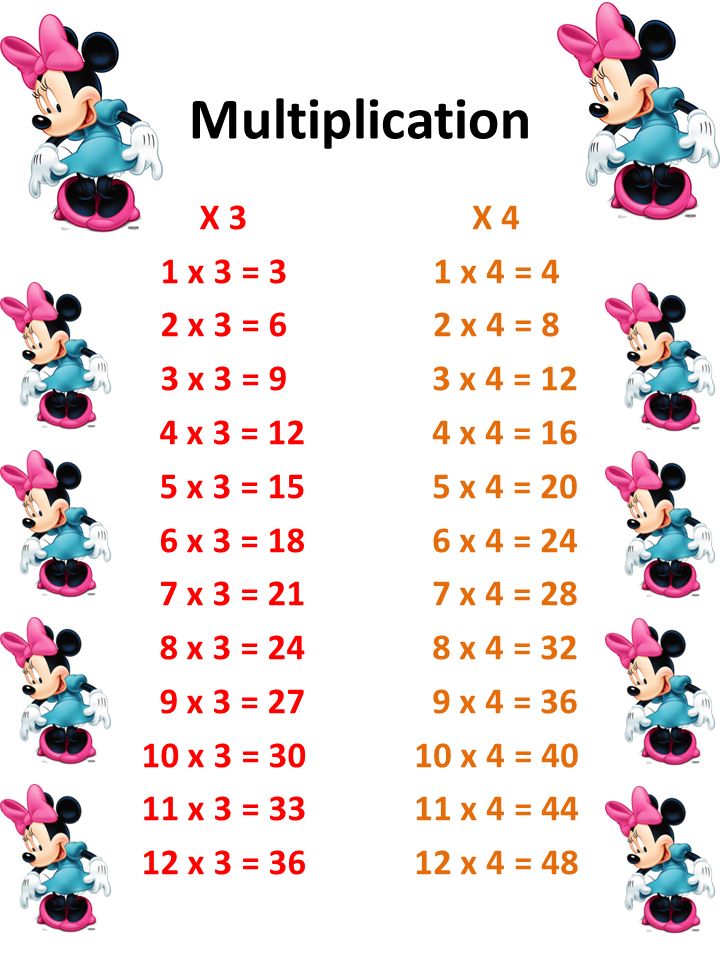



Multiplication X 1 1 X 1 1 2 X 1 2 3 X 1 3 4 X 1 4 5 X 1 5 6 X 1 6 7 X 1 7 8 X 1 8 9 X 1 9 10 X 1 X 1 X 1 12 X Ppt Video Online Download
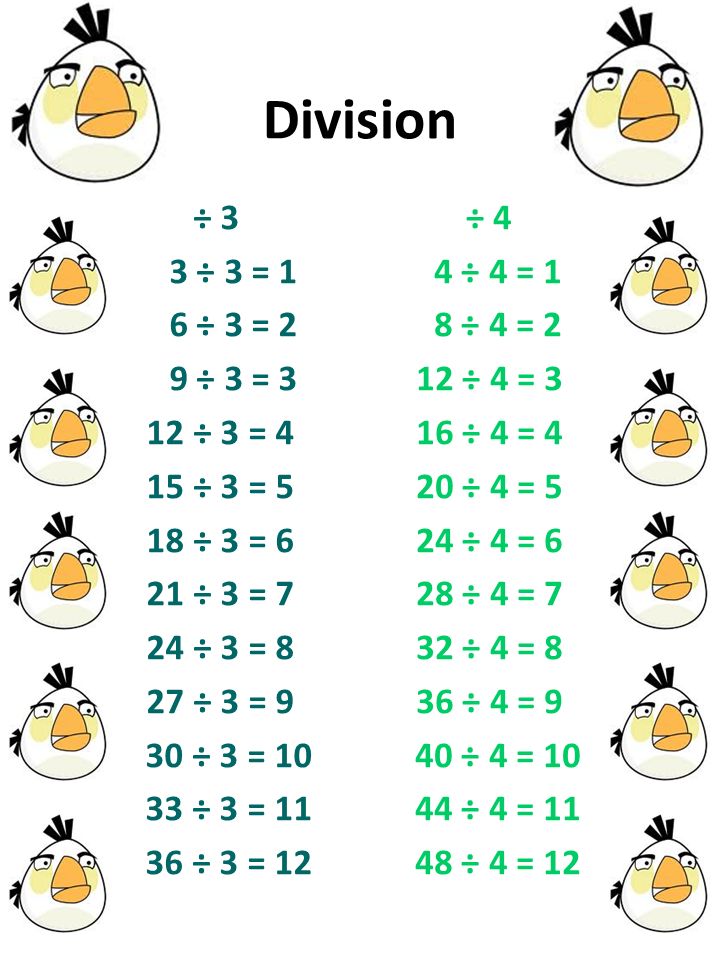



Division 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 3 1 3 4 1 4 5 1 5 6 1 6 7 1 7 8 1 8 9 1 9 10 1 1 1 12 2 2 2 Ppt Video Online Download




Answered Let A H T B 1 2 3 4 5 6 Bartleby
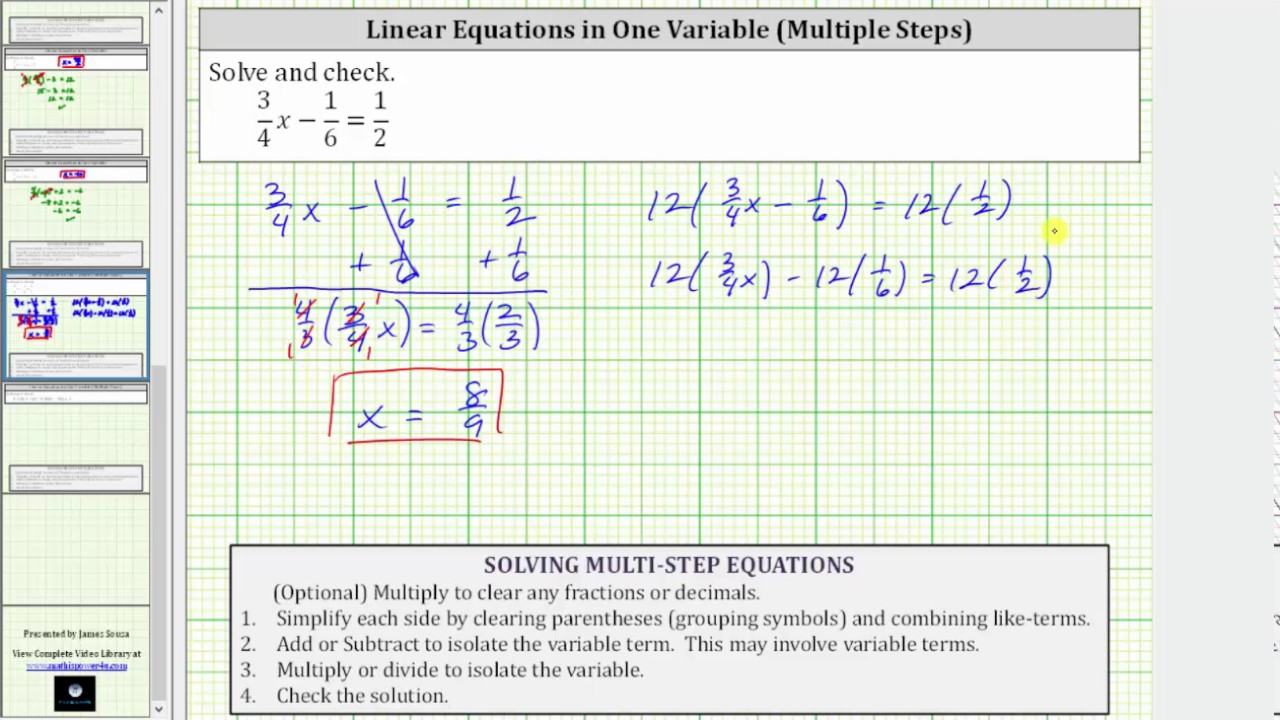



Solve A Linear Equation With Fractions 3 4x 1 6 1 2 Youtube




Year 3 Maths Term 2 Week Ppt Download



What Is 1 3 1 6
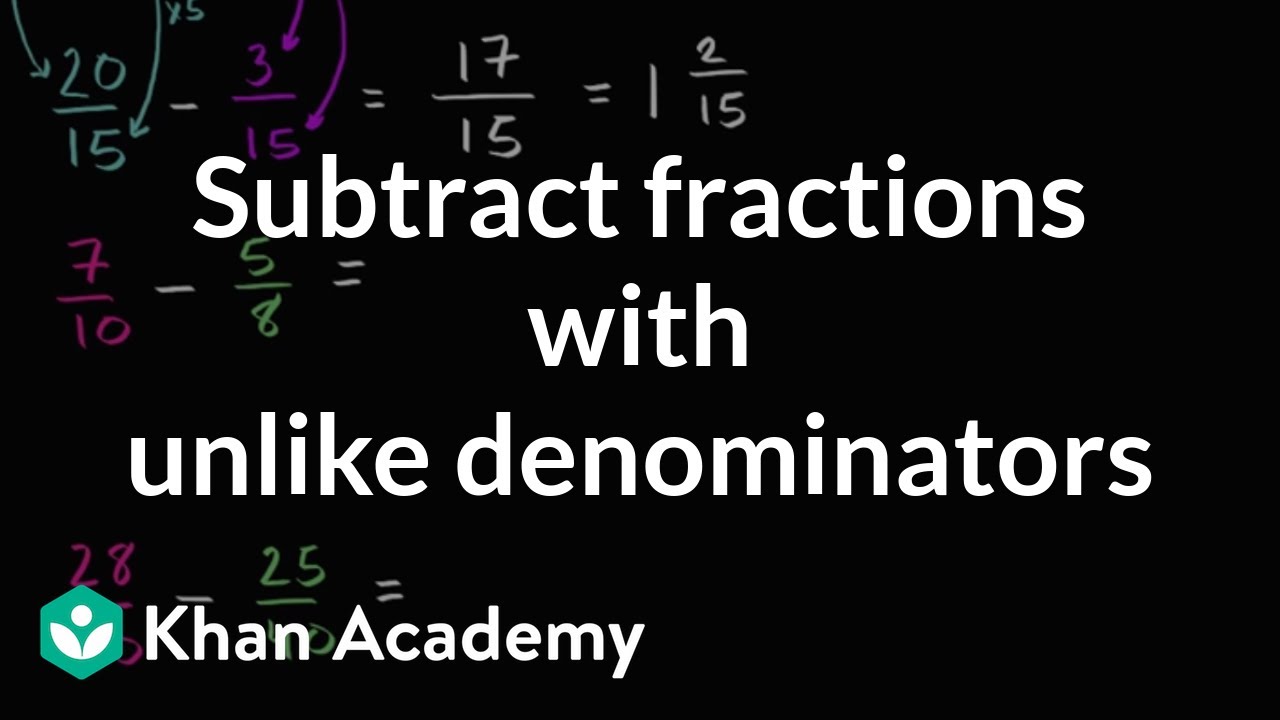



Subtracting Fractions With Unlike Denominators Video Khan Academy




The Relations R 1 4 2 2 3 2 3 3 Chegg Com




Simplify 64 1 6 216 1 3 81 1 4 512 1 3 16 1 4 9 1 2




Fraction Calculator All Operations With Explanation




Simplify 1 1 2 1 3 1 6 3 4 1 3 Brainly In




Breaking A Fraction Into A Unique Sum Of Two Distinct Unit Fractions By Keith Mcnulty Cantor S Paradise




Solve A 2 3 1 7 B 3 10 7 15 C 4 9 2 7 D 5 7 1 3 E 2 5 1 6 F 4 5 2 3 G 3 4 1 3 H 5 6 Brainly In
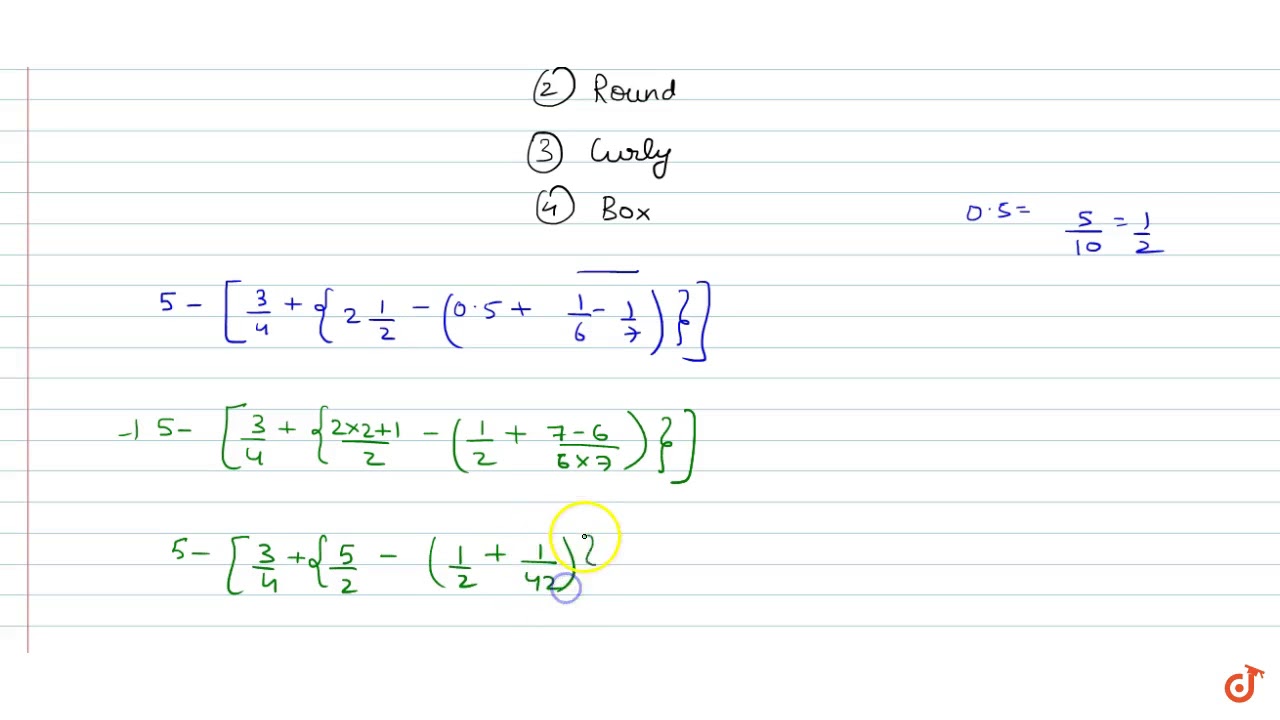



Simplify 5 3 4 2 1 2 0 5 Bar 1 6 1 7 Youtube




Ex 13 2 14 Given P A 1 2 P B 1 3 Find Problem Is



How To Prove That 1 1 5 2 9 3 13 4 E 3 Quora




Find The Value Of In The Following 1 2 3 2 7xx 7 1 1 4xx2 3 1 6 A 0 006 B 1 6 C 0 6 D 6




1 1 3 1 1 4 1 1 5 1 1 6 1 1 N Youtube




Amazon Com Eai Education Fraction Circles Numbered Set Of 51 Toys Games
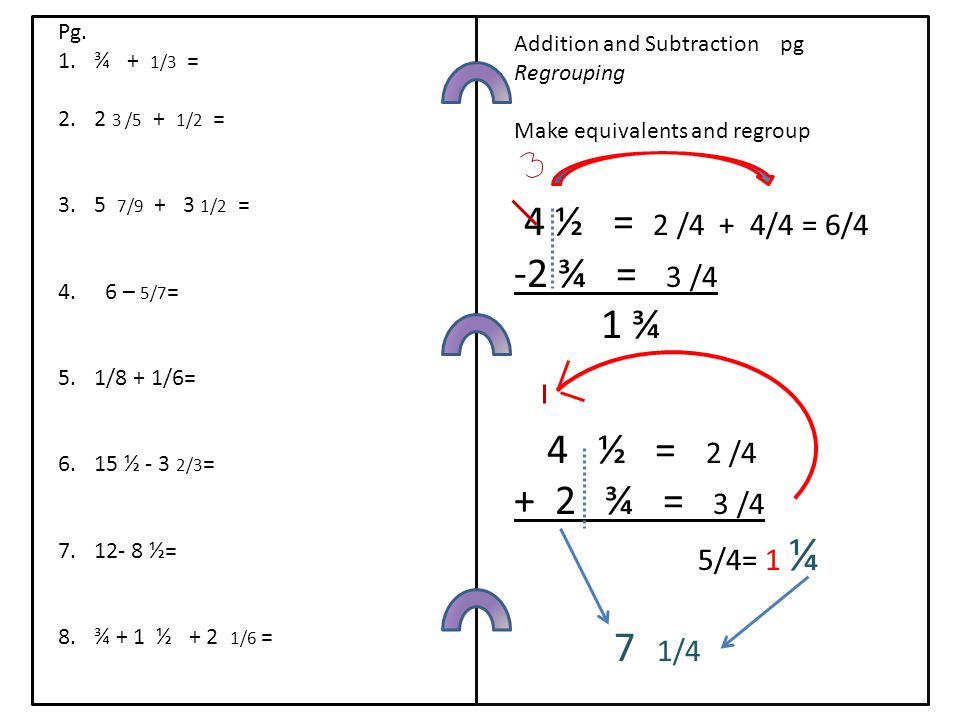



6 6 Most Often As Word Problems Ppt Download




Can You Solve It Complete The Equation 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 16 Mathematics The Guardian




1 3 4 5 9 7 16 9 25 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 Chegg Com




If 1 2 1 3 1 6 3 X Then X 1 2




Starter Questions Q 1 Calculate Q 2 Q
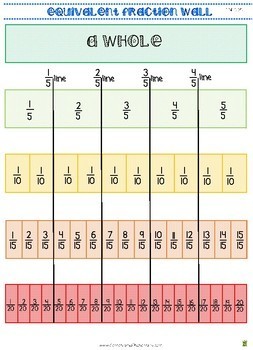



Fraction Wall Anchor Chart Poster 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 To 1 4 N F 1



Change The Following Groups Of Fractions To Like Fractions I 1 3 2 5 3 4 1 6 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Simplify 5 3 4 2 1 2 0 5 Bar 1 6 1 7




Question 1 3 1 0 A 35 Points A 2 6 2 3 10 Use Chegg Com



Q Tbn And9gcqu8faeki7cypmf8hq56iqys Li9ev6fccwfo0eyp86m5fli1 Usqp Cau




Simplify 4 1 X 3 1 2 Ii 5 1 6 1 3 2 1 3 1 1 Iv 3 1 X 4 1 1 X 5 1 4 1 5 1 3 1



What Is The Sum Of The Series Math 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 Math Up To Infinity How Can It Be Calculated Quora




Tabel Pembagian 1 Sampai 100




Evaluate 6 1 8 1 1 2 1 3 1 1 Brainly In



What Is 1 6 2 3



3




Understanding Conditional Probability Mathematics Stack Exchange



What Is Half Of 1 3 Cup Socratic




2 1 3 1 1 6 1 8 1 1 Simplify Brainly In




1 1 1 3 1 2 1 4 1 5 1 4 1 6 Determine Whether The Sequence Converges Or Diverges Youtube




Adding And Subtracting Fractions Ppt Download




If X 1 2 1 3 2 2 3 Show That X 3 3x 2 3x 1 0 Cbseassistance




Find The Value Of 1 1 2 3 3 1 2 1 1 6 3 1 2 A 3 B 4 21 C 8 21 D 13 21



Simplify I 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 6 Ii 24 35 6 7 5 7 X 3 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
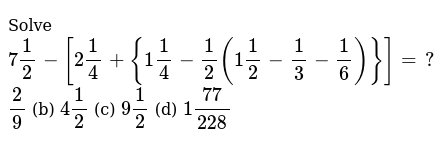



Solve 7 1 2 2 1 4 1 1 4 1 2 1 1 2 1 3 1 6 2 9 B 4 1 2 C 9 1 2 D 1 77 228




Ex 7 6 1 Solve A 2 3 1 7 B 3 10 7 15 C 4 9 2 7 D 5 7




Selina Solutions Concise Maths Class 7 Chapter 3 Fraction Including Problems Exercise 3c Get Pdf



What Is The Value Of The Product 1 1 2 1 1 3 1 1 4 1 1 5 Quora




Beginner Fractions Pizza Graphics 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 1 8



What Is 1 5 1 3
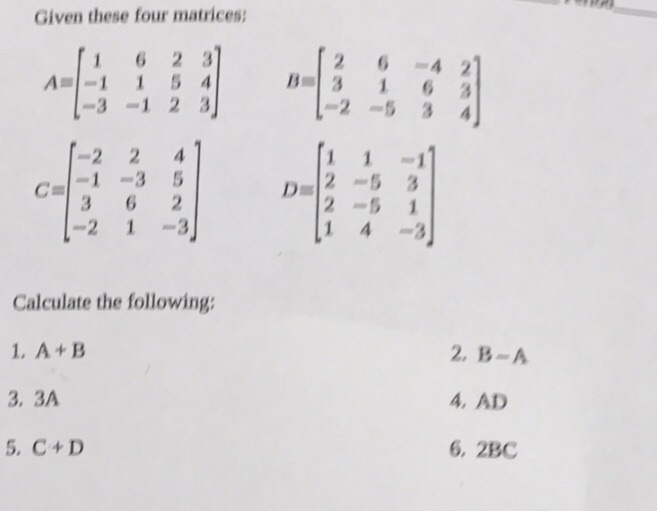



Given These Four Matrices A 1 1 3 6 1 1 2 5 2 Chegg Com




Find The Product Ab For A A 1 1 3 1 B 5 Chegg Com



What Is The Infinite Sum Of The Series 1 1 1 3 1 6 1 10 1 15 Quora




Determine Whether The Series Is Convergent Or Chegg Com




Example 18 Solve 5 X 1 1 Y 2 2 6 X 1 3 Y 2 1 Examples




Calameo Tableau Des Complementaires




Solve The Following 5 1 2 1 3 1 4 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 1lw16x22




Ex 7 6 1 Solve A 2 3 1 7 B 3 10 7 15 C 4 9 2 7 D 5 7



What Is 1 6 1 2



What Is 1 3 1 6




1 1 3 1 6 1 10 1 15 Most Difficult Series Made Simple Iit Jee Ib Math 2 Youtube



Brazilian Cotton Being The Report Of The Journey Of The International Cotton Mission Through The Cotton States Of Sa O Paulo Minas Geraes Bahia Alaga As Sergipe Pernambuco Parahyba Rio Grande Do Norte



1




4 5 1 6 2 3 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 3 2 1 1 2 Gauthmath
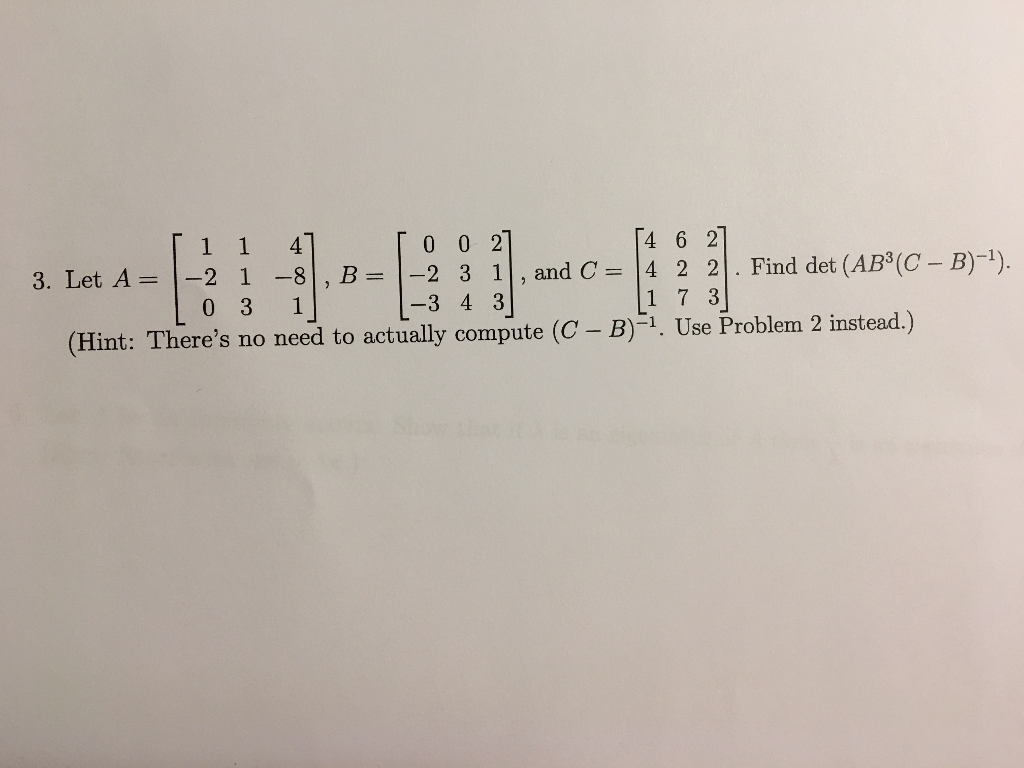



Let A 1 2 0 1 1 3 4 8 1 B 0 2 3 0 3 4 Chegg Com




Ex 2 3 1 Find I 1 4 Of A 1 4 B 3 5 C 4 3 Ii 1 7 Of




What Is The Average 1 2 1 3 And 1 6 Brainly In




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 8 Chapter 1 Rational Numbers Download Free Pdf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿